Learing ISTQB Advansed Security Tester
Test automation devops
https://www.istqb.org/certification-path-root/advanced-security-tester.html
シラバスの中から興味ある部分を翻訳+追加で調べてみます。
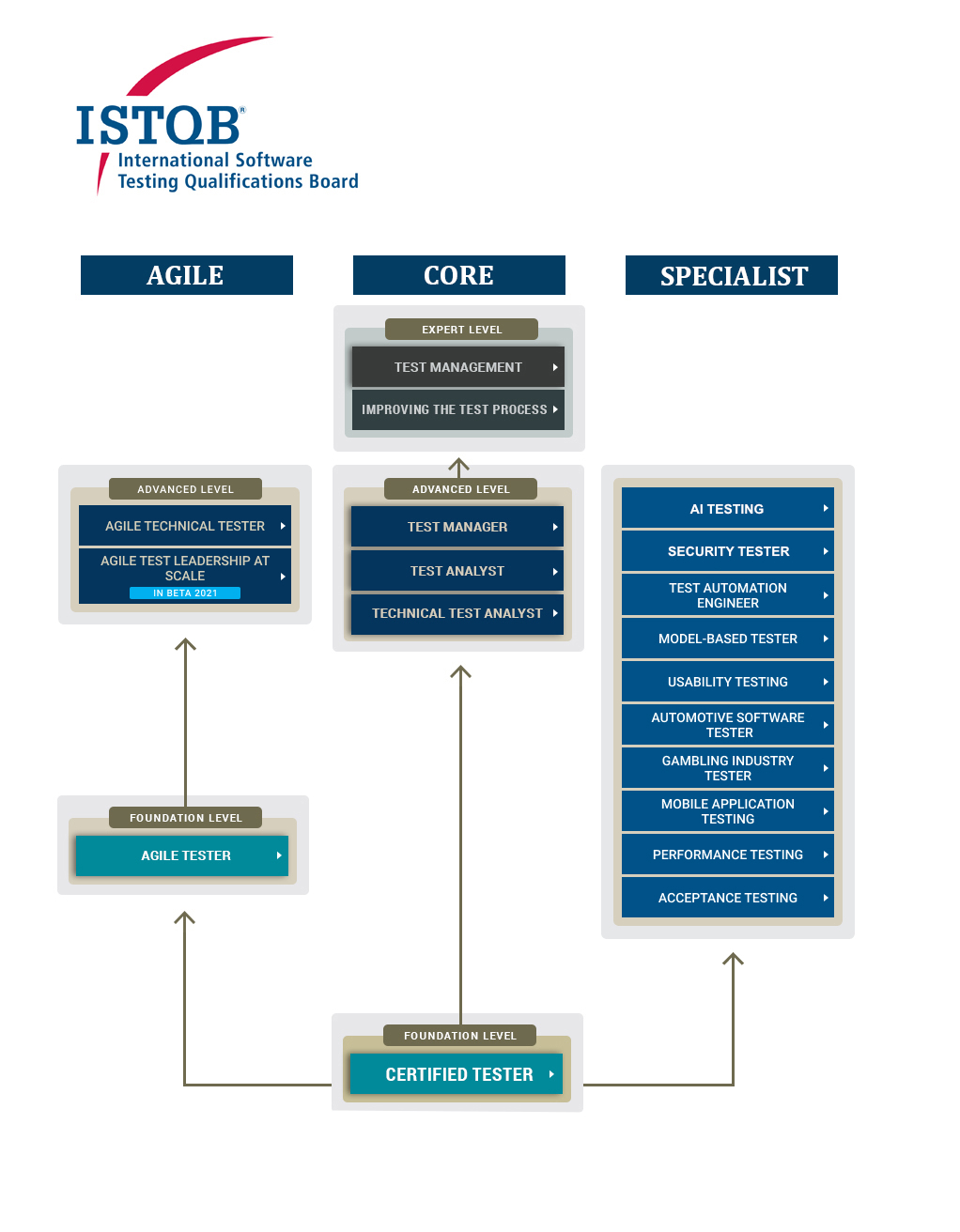
ISTQBの全体像
Advanced levelはFoundation Levelの上位にあたります。
内容もだけど英語が難しい。。
引用元:https://www.istqb.org/portfolio_map/images/istqb-portfolio-image.jpg
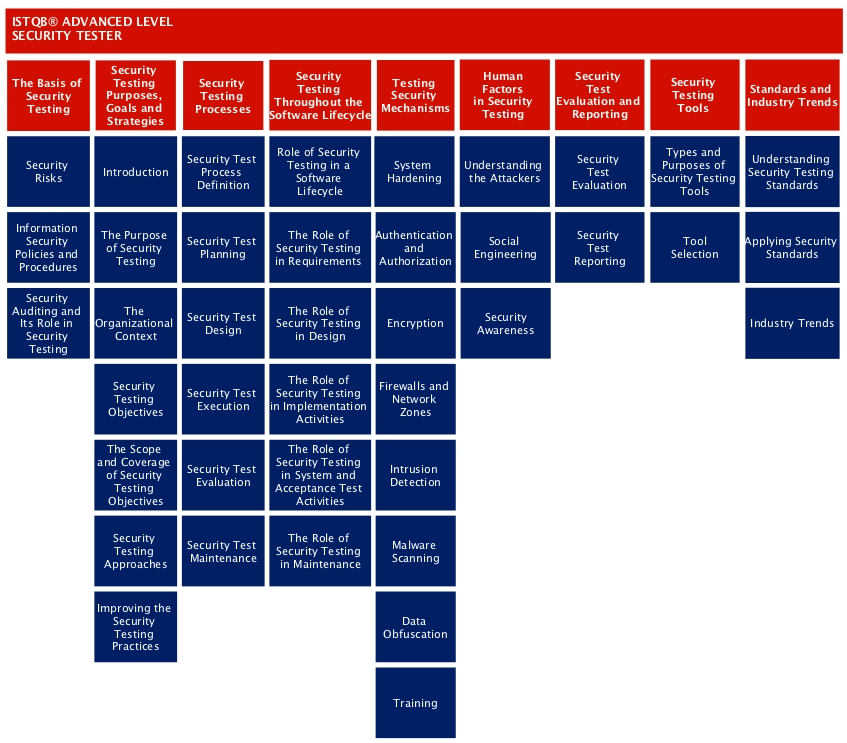
Security Testerのコンテンツ
引用元:https://www.istqb.org/images/security-tester-contents.png
シラバスを読む
引用元: https://www.istqb.org/downloads/category/46-advanced-level-security-tester.html
The Basis of Security Testing - 105 mins
- 1.1 Security Risks
- 1.1.1 The Role of Risk Assessment in Security Testing
- 1.1.2 Asset Identification
- 1.1.3 Analysis of Risk Assessment Techniques
- 1.2 Information Security Policies and Procedures
- 1.2.1 Understanding Security Policies and Procedures
- 1.2.2 Analysis of Security Policies and Procedures
- 1.3 Security Auditing and Its Role in Security Testing
- 1.3.1 Purpose of a Security Audit
- セキュリティ監査で検出される可能性のある項目と検出例
- 不適切な物理的セキュリティ
- 以下のようなセキュリティ・ポリシーが定義されている
- すべての顧客データの暗号化
- 保管時と送信時の両方で、すべての顧客データを暗号化
- 監査の過程で、毎週1回、顧客情報ファイルが物理的なレポートによって全マネージャーに送られていることが判明。この報告書は毎週廃棄されますが、一部のマネージャーは物理的な報告書を不注意にもゴミ箱に捨てており、ゴミ箱を調べようとする誰もが見つけられる場所に置いていることが判明しました。
- 以下のようなセキュリティ・ポリシーが定義されている
- 不適切なパスワード管理
- セキュリティポリシーでは、各ユーザが30日ごとにパスワードを変更することを求めている
- セキュリティ監査の結果、パスワードは変更されているものの、多くのユーザは毎月「PasswordA」と「PasswordB」を交互に使用していることが判明します。(パスワードの履歴は、パスワード監査ツールの一般的な機能です)。)
- ユーザー権限と共有権限の管理が不十分であること
- 否定的な所見の例としては、ユーザが自分の仕事を遂行するのに必要以上のアイテムへのアクセス権を与えられている場合が挙げられる。別の例としては、個人のユーザーのファイルが非公開であるべきなのにネットワーク上で共有されている場合が挙げられます。これは、ノートPCを使用しているユーザー、特に自宅や公共の場所でWi-Fi接続を利用してイントラネットにアクセスしているユーザーにとって、特に懸念すべきことです。
- サーバーレベルのセキュリティが不十分である
- 具体的な監査項目
- ポートの割り当てとセキュリティ
- データの保護
- ユーザーアカウント(ログイン情報やその他の機密情報)の保護
- 具体的な監査項目
- ベンダーのセキュリティアップデートの適用が不十分であること
- 不適切な侵入検知メカニズム
- セキュリティ侵害が発生した場合の対応計画の不備
- 不適切な物理的セキュリティ
- 1.3.2 Risk Identification, Assessment and Mitigation
- 1.3.3 People, Process and Technology
Security Testing Purposes, Goals and Strategies - 130 mins
- 2.1 Introduction
- 2.2 The Purpose of Security Testing
- 2.3 The Organizational Context
- 2.4 Security Testing Objectives
- 2.4.1 The Alignment of Security Testing Goals
- 2.4.2 Identification of Security Test Objectives
- 2.4.3 The Difference Between Information Assurance and Security Testing
- 情報保証(IA)とセキュリティテストの違い
- IAはセキュリティテストより広い範囲を意味する単語
- 品質保証とソフトウェアテストの関係に似ている
- 情報保証(Information Assurance)とは
- 情報保証とは、情報を保証し、情報の使用、処理、保存、および送信に関連するリスクを管理することです。情報保証には、ユーザーデータの整合性、可用性、信頼性、否認防止、および機密性の保護が含まれます。 IAには、デジタル保護だけでなく、物理的な手法も含まれます。
- 参考:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Information_assurance
- セキュリティテストとは
- 「システムのセキュリティ機能が設計どおりに実装されており、提案されたアプリケーション環境に適しているかどうかを判断するために使用されるプロセス」です。 [MDA1]
- 2.5 The Scope and Coverage of Security Testing Objectives
- 2.6 Security Testing Approaches
- 2.6.1 Analysis of Security Test Approaches
- 2.6.2 Analysis of Failures in Security Test Approaches
- 2.6.3 Stakeholder Identification
- 2.7 Improving the Security Testing Practices
Security Testing Processes - 140 mins
- 3.1 Security Test Process Definition
- 3.1.1 ISTQB Security Testing Process
- 基本的にはソフトウェアテストのプロセスと同じ
- 結果の評価部分に差分あり
- 結果の評価とレポート - 新しい脅威をできるだけ早く報告するためにテスト実行と並行して実行されることがよくあります
- 3.1.2 Aligning the Security Testing Process to a Particular Application Lifecycle Model
- → 特定のアプリケーションのライフサイクルに合わせてプロセスを調整する
- 3.1.1 ISTQB Security Testing Process
- 3.2 Security Test Planning
- 3.2.1 Security Test Planning Objectives
- 2つの側面にフォーカスするのが一般的
- 設計されたセキュリティ防御が実装され、設計どおりに機能することを確認する
- リスク分析に基づく
- アプリケーションの開発中に脆弱性が導入されていないことを確認する
- 品質保証のアクティビティとベストプラクティスで回避することができる
- 開発チームのプラクティスの評価から始める
- この結果に基づいて追加のセキュリティテストの導入を選択する
- 設計されたセキュリティ防御が実装され、設計どおりに機能することを確認する
- 2つの側面にフォーカスするのが一般的
- 3.2.2 Key Security Test Plan Elements
- 下記の質問で主要な要素を決定することができる
- スコープの確認する
- テスト実行者について確認する
- 通常のテストスケジュールを考慮して適切なスケジュールを確定する
- 実行するタスクと必要な時間を定義する
- セキュリティテスト環境について定義する
- セキュリティテスト活動のための承認と承認を取るための準備
- 3.2.1 Security Test Planning Objectives
- 3.3 Security Test Design
- 3.3.1 Security Test Design
- 機能的なものと構造的なものに分けて考えられる
- 例. 電子商取引のウェブサイトのセキュリティテストの場合
- 機能的:SQLインジェクション、アカウントハーベスティング、パスワードクラッキング
- 構造的:バッファーオーバーフローの状態で攻撃者がメモリの障害を利用してアクセス可能になってしまう
- 例. 電子商取引のウェブサイトのセキュリティテストの場合
- 機能的なものと構造的なものに分けて考えられる
- 3.3.2 Security Test Design Based on Policies and Procedures
- 3.3.1 Security Test Design
- 3.4 Security Test Execution
- 3.4.1 Key Elements and Characteristics of an Effective Security Test Environment
- リスクが有るため、通常のテスト環境とは分離した環境が必要
- 3.4.2 The Importance Of Planning and Approvals in Security Testing
- 3.4.1 Key Elements and Characteristics of an Effective Security Test Environment
- 3.5 Security Test Evaluation
- 3.6 Security Test Maintenance
- → 新しいリスクの発見やツールの登場のよりプロセスは見直す必要があるため変更しやすいプロセスにしておく必要がある
Security Testing Throughout the Software Lifecycle - 225 mins
- 4.1 The Role of Security Testing in a Software Lifecycle
- セキュリティも開発していく中で設計のセキュリティレビューや検証によって達成されるもの
- 開発ライフサイクルの中で行う必要がある
- 4.1.1 The Lifecycle View of Security Testing
- 4.1.2 Security-Related Activities in the Software Lifecycle
- 4.2 The Role of Security Testing in Requirements
- 4.3 The Role of Security Testing in Design
- 4.4 The Role of Security Testing in Implementation Activities
- 4.4.1 Security Testing During Component Testing
- 4.4.2 Security Test Design at the Component Level
- 4.4.3 Analysis of Security Tests at the Component Level
- 4.4.4 Security Testing During Component Integration Testing
- 4.4.5 Security Test Design at the Component Integration Level
- 4.5 The Role of Security Testing in System and Acceptance Test Activities
- 4.5.1 The Role of Security Testing in System Testing
- 4.5.2 The Role of Security Testing in Acceptance Testing
- 4.6 The Role of Security Testing in Maintenance
Testing Security Mechanisms - 240 mins.
- 5.1 System Hardening
- → ITシステムの脆弱性を減らしてセキュリティレベルを向上させること
- 5.1.1 Understanding System Hardening
- 5.1.2 Testing the Effectiveness of System Hardening Mechanisms
- 5.2 Authentication and Authorization
- 5.2.1 The Relationship Between Authentication and Authorization
- 5.2.2 Testing the Effectiveness of Authentication and Authorization Mechanisms
- 5.3 Encryption
- 5.3.1 Understanding Encryption
- 5.3.2 Testing the Effectiveness of Common Encryption Mechanisms
- 5.4 Firewalls and Network Zones
- 5.4.1 Understanding Firewalls
- 5.4.2 Testing Firewall Effectiveness
- 5.5 Intrusion Detection
- 5.5.1 Understanding Intrusion Detection Tools
- 5.5.2 Testing the Effectiveness of Intrusion Detection Tools
- 5.6 Malware Scanning
- 5.6.1 Understanding Malware Scanning Tools
- 5.6.2 Testing the Effectiveness of Malware Scanning Tools
- 5.7 Data Obfuscation
- 5.7.1 Understanding Data Obfuscation
- 5.7.2 Testing the Effectiveness of Data Obfuscation Approaches
- 5.8 Training
- 5.8.1 The Importance of Security Training
- 5.8.2 How to Test the Effectiveness of Security Training
Human Factors in Security Testing - 105 mins.
- 6.1 Understanding the Attackers
- 6.1.1 The Impact of Human Behavior on Security Risks
- 6.1.2 Understanding the Attacker Mentality
- 6.1.3 Common Motivations and Sources of Computer System Attacks
- 6.1.4 Understanding Attack Scenarios and Motivations
- 6.2 Social Engineering
- 6.3 Security Awareness
- 6.3.1 The Importance Of Security Awareness
- 6.3.2 Increasing Security Awareness
Security Test Evaluation and Reporting - 70 mins
- 7.1 Security Test Evaluation
- 7.2 Security Test Reporting
- 7.2.1 Confidentiality of Security Test Results
- → テスト結果からシステムの脆弱性がわかってしまう。知る必要がある人にだけ共有すること。
- 7.2.2 Creating Proper Controls and Data Gathering Mechanisms for Reporting Security Test Status
- 7.2.3 Analyzing Interim Security Test Status Reports
- 7.2.1 Confidentiality of Security Test Results
Security Testing Tools - 55 mins
- 8.1 Types and Purposes of Security Testing Tools
- 8.2 Tool Selection
- 8.2.1 Analyzing and Documenting Security Testing Needs
- 8.2.2 Issues with Open Source Tools
- 8.2.3 Evaluating a Tool Vendor’s Capabilities
Standards and Industry Trends - 40 mins
- 9.1 Understanding Security Testing Standards
- 9.1.1 The Benefits of Using Security Testing Standards
- 9.1.2 Applicability of Standards in Regulatory Versus Contractual Situations
- 9.1.3 Selection of Security Standards
- 9.2 Applying Security Standards
- 9.3 Industry Trends
- 9.3.1 Where to Learn of Industry Trends in Information Security
- 9.3.2 Evaluating Security Testing Practices for Improvements